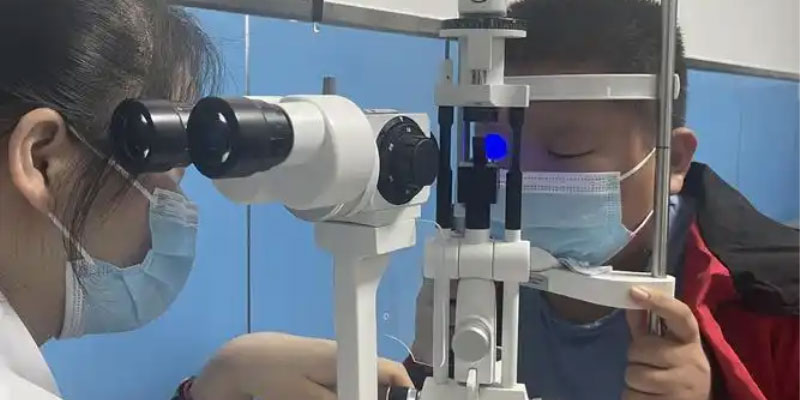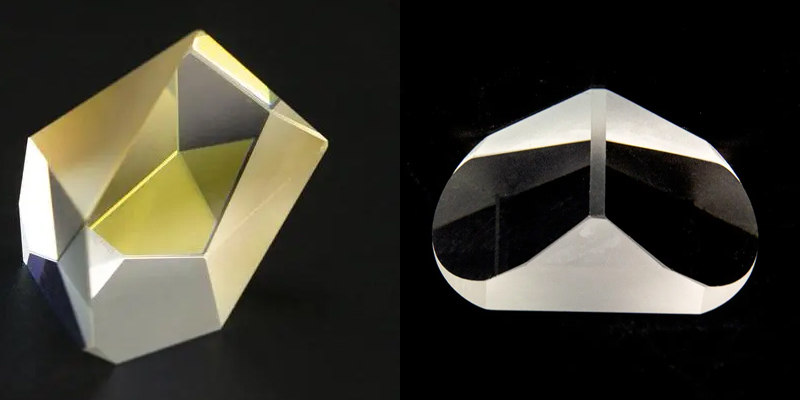
Paul prisms and roof prisms are common optical instruments, and there are some differences in their optical properties, fields of application and effects of use. The following will introduce the characteristics of Paul’s prisms and roof prisms respectively, and compare their advantages and disadvantages.
1.Paul Prism
A Paul’s prism is an optical instrument with four refracting surfaces containing two right-angled triangular prisms and two beveled prisms. Its main role is to split a beam of light into two mutually perpendicular beams, and to ensure that the spatial position of the two beams of light is stable and unchanged. Therefore, Paul’s prisms are widely used in the fields of optical measurement, optical interference and optical imaging.
The advantages of Paul’s prisms lie in their simple structure, easy processing and manufacturing, low cost. In addition, because of its high transmittance and small aberrations, Paul prisms perform well in optical performance. However, Paul prisms are large in size and not light enough to be used, and their beam splitting effect is also affected by the angle, resulting in insufficient measurement accuracy.
This is called the “dispersion” effect. Using this effect, you can use the prism to add rainbows to your work. Whether it’s a simple, crude rainbow in the face for a portrait or as a background for a still life, the effect is great.

2.Roof Prism
A roof prism is an optical instrument with the shape of a roof, which is made by attaching two triangular pieces of glass. The main function of a roof prism is to split a beam of light into two perpendicular beams and to ensure that the spatial position of the two beams remains stable. Unlike Paul’s prisms, roof prisms reflect light once during the splitting process, making them more compact, smaller and lighter to use.
The advantages of roof prisms are their compactness, small size and ease of use. In addition, because its beam splitting effect is not affected by the angle, the ridge prism’s measurement accuracy is high. However, ridge prisms are relatively expensive and difficult to manufacture, and their transmittance is slightly lower than that of Paul’s prisms.
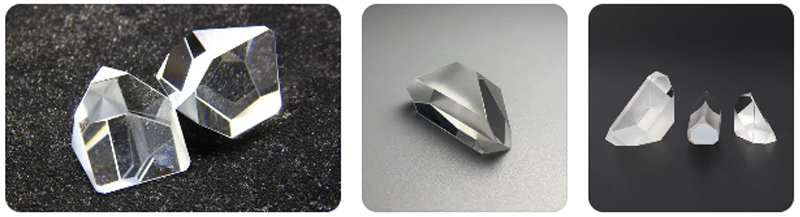
To summarize, Paul prisms and roof prisms have their own advantages and disadvantages and are suitable for different application scenarios. If you need to use low-cost, simple structure of the optical instrument, you can choose Paul prism; if you need to use small size, high precision optical instrument, you can choose the roof prism. Regardless of which optical instrument to choose, the choice should be made according to the actual needs to ensure that the best use of the effect.
optlenses
Related posts
Dichroic Mirror: A Reliable Assistant in Gemstone Identification
What is the Iris Diaphragm Microscope?
What is an collimator and its application fields?
Confocal Microscopy:The Pioneer of High-Precision Imaging