Basic working principle of optical lenses
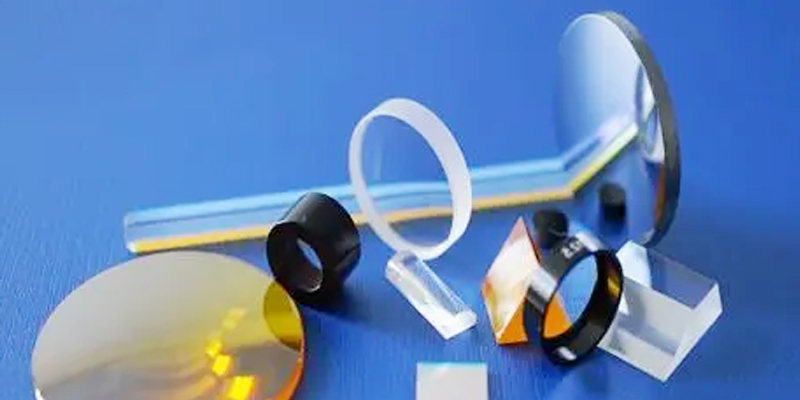
A optcal lens is made according to the law of refraction of light. It is an optical element made of a transparent substance (such as glass, crystal, etc.). Lens is a refracting mirror, its refracting surface is two spherical surface (part of the sphere), or a spherical surface (part of the sphere) a plane of the transparent body. The image formed by the lens has a real image and an imaginary image. Lens can be widely used in security, automotive, digital cameras, lasers, optical instruments and other fields, with the continuous development of the market, lens technology is also more and more widely used. Imaging principle of lens
A transparent object is said to be a lens if both of its interfaces are spherical, or one interface is spherical and the other is flat.
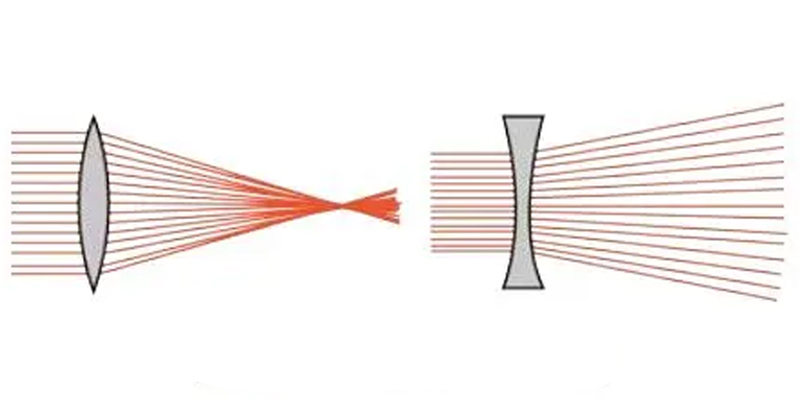
Imaging principle of lens
If both interfaces of a transparent object are spherical, or one interface is spherical and the other is flat, the object is called a lens. Lenses whose central portion is thicker than their edges are called convex lenses, and are classified by the shape of their cross sections as biconvex, plano-convex, or concave-convex. They are used in the equidistant image method of focal length measurement, photocopiers, slide projectors, projectors, projectors, and so on. It has the function of dispersing light. The lens whose central part is thinner than the edge is called concave lens, and it can be divided into biconcave, plano-concave and concave-convex depending on the shape of its cross-section. Applications include myopic glasses, cat’s eyes (door mirrors), flashlights, etc.
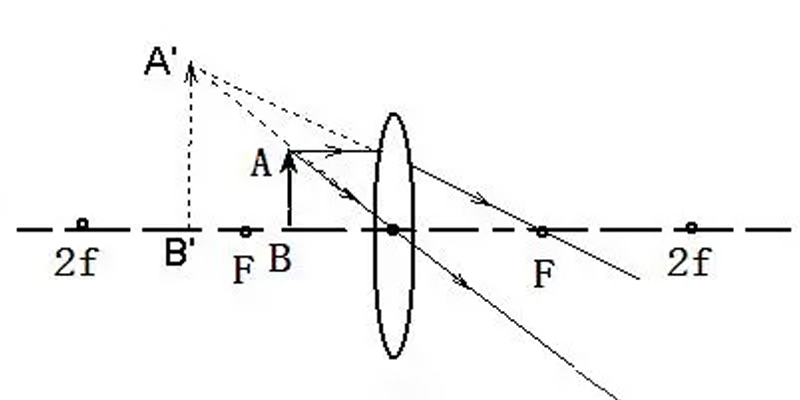
The line passing through the center of curvature of the two spherical surfaces of the lens is called the main optical axis or principal axis of the lens. There is a special point on the principal axis through which light travels in the same direction, and this point is called the optical center of the lens, indicated by the letter “O”. A convex lens converges light rays parallel to the principal optical axis at a point on the principal optical axis, which is called the focal point. A convex lens has a focal point on each side, which is symmetrical with respect to the center of light, and is denoted by the letter “F”. The distance from the focal point to the center of the convex lens is called the focal length and is denoted by the letter “f”. A convex lens is also called a converging lens because of its ability to converge light rays. Light directed to a concave lens becomes divergent after passing through the concave lens, which is also called a diverging lens because of its ability to diverge light rays.
When the distance from the object to the convex lens is greater than 2 times the focal length, it becomes an inverted, reduced solid image; when the distance from the object to the convex lens is between 2 times the focal length and the focal length, it becomes an inverted, magnified solid image; when the distance from the object to the convex lens is less than the focal length, it becomes an orthogonal, magnified virtual image.
optlenses
Related posts
Dichroic Mirror: A Reliable Assistant in Gemstone Identification
What is the Iris Diaphragm Microscope?
What is an collimator and its application fields?
Confocal Microscopy:The Pioneer of High-Precision Imaging