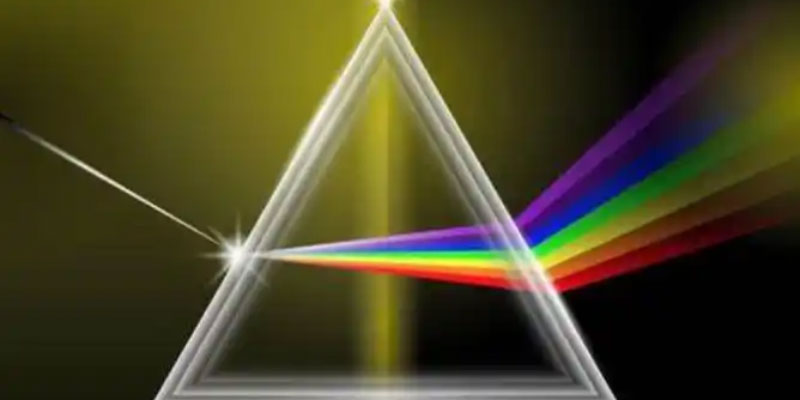
1. the filter’s basic idea
Usually composed of glass or plastic, filters can be created in three different ways: using glass coating, colored glass, or plastic materials. Special colors are then added. Normal glass and air have similar refractive indices, so all light can pass through. However, after dyeing, the molecular structure changes, and the refractive index changes as well. For example, when white light passes through a blue filter, it turns green, and very little red or green light passes through the filter; most of it is absorbed. Second, there is a specific production technique that involves creating a filter on a semiconductor wafer in order to improve the filter’s adherence and stop light interference. This process entails first creating a protective, metal, and dielectric layer on a semiconductor wafer, followed by the sequential production of several filters.
2.the characteristics of the filter
Filters are mainly divided into two types: colour filters and thin-film filters.
Colour filters are usually used in broadband photometry or stellar spectrographs, mainly used to isolate the overlapping spectral levels. One of their distinctive features is that they can be made in fairly large sizes, which makes them useful in a wide range of optical applications.
Thin film filters, on the other hand, are mostly used for infrared filtering, which transmits at longer wavelengths. It is formed on a specific substrate, the use of vacuum coating method alternately with a specific thickness of the high refractive index or low refractive index of the metal – dielectric – metal film, or all dielectric film, thus constituting a low-level, multi-level tandem solid Fabry-Perot interferometer. This structure gives thin film filters unique filtering properties.
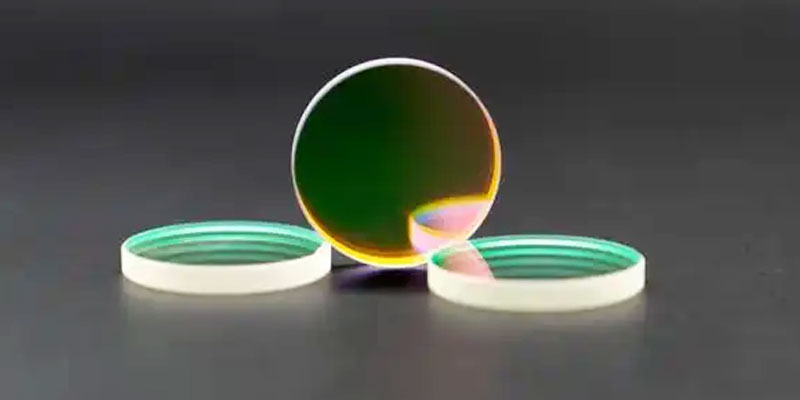

3.the classification of common filters
According to the spectral band, can be divided into ultraviolet filters, visible filters and infrared filters.
According to the spectral characteristics are divided into: bandpass filters, cut-off filters, spectral filters, neutral density filters, reflection filters;
According to the selected band of light allowed to pass, while the light outside the passband is cut off and divided into bandpass filters, at the same time to the centre wavelength (CWL), half-height width (FWHM) as its optical indicators. It is divided into narrowband and wideband.
According to the membrane layer material, there are soft film filters and hard film filters, soft film filters are commonly used in biochemical analysers, hard film filters are widely used in laser systems.
In addition to the short-wave and long-wave pass to distinguish between short-wave pass: shorter than the selected wave through the light, such as infrared cut-off filters. Long wavelength pass, longer than the selected wavelength of light through, shorter than the wavelength of the light cut-off, such as infrared transmission filters.
optlenses
Related posts
What is the group velocity dispersion?
Cylinder Lens:The Function and Application Areas
What is The Interferometers?
Dichroic Mirror: A Reliable Assistant in Gemstone Identification