Photonic Crystal Fiber (PCF) is a kind of optical fiber with special pore structure, which can realize the optimization of optical performance and transmission characteristics through the precise control of the structure of the fiber.The unique design and advantages of PCF make it show a broad application prospect in the fields of optical communication, optical sensing, and laser technology.
1.Background of fiber-optic technology
We can now enjoy a convenient network environment, behind an outstanding technical achievement of the last century – fiber-optic technology. This technology takes light waves as the information carrier, and uses optical fibers, i.e. optical fibers, for high-speed transmission, making it possible to instantly transmit a large amount of information, with a transmission capacity comparable to the contents of thousands of books and a distance of up to hundreds of kilometers. There has been a “Scientific American” magazine will be fiber-optic communications as one of the four most significant post-World War II invention, and pointed out that, if not for the birth of fiber-optic communications, today’s Internet and communication networks may be difficult to exist.
- Development and Limitations of Fiber Optic Technology
Fiber optic technology initially used primarily quartz as the material for transmitting signals, but over time the technology has evolved to use a variety of materials such as phosphates, borates, sulfides, fluorides, and even plastics. Despite the changing materials, the basic principles and structure of optical fibers have remained the same, following the theory of total reflection within light and using a unique design of core and cladding. However, with the rapid increase in technology, especially the demand for Internet speeds, traditional optical fibers are outperforming. To meet this challenge, fiber optic communication systems are constantly pursuing higher transmission rates, longer transmission distances, and greater capacity. However, limited by factors such as structure, material and manufacturing process, the performance improvement of traditional optical fibers appears to be relatively slow.
- The Emergence of Photonic Crystal Fiber
It is against this background that the new fiber optic technology of Photonic Crystal Fiber (PCF) came into being and became a new hope for the development of the industry.
2.Characteristics of Photonic Crystal Fiber

- Photonic crystals and their fundamentals
Photonic crystals, an artificially created dielectric structure, are made up of unique photonic crystals (PCs) by periodically arranging dielectrics with different refractive indices. Similar to the forbidden bands of electrons in semiconductors and insulators, photonic crystals can be fabricated in certain materials to prohibit the propagation of light within a certain range, either in a specific direction or omni-direction. Because of this, it exhibits Photonic Band Gap (PBG) properties, and is therefore also known as Photonic Band Gap material or Photonic Crystal PBG material.
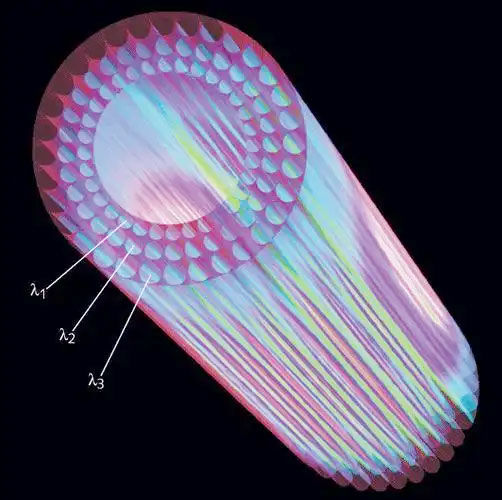
The concept of photonic crystal fiber (PCF) was first introduced by Russell of Bath University, UK, in 1992. The periodic structure of the PCF is altered by introducing defects in the center of the PCF, for example, by incorporating air holes arranged periodically in the cladding. In this way, the defect location forms the core of the PCF, allowing the incident light to be confined to the core for transmission without entering the PC cladding. This is the basic principle of photonic crystal fiber.
- Characteristics of Photonic Crystal Fibers of Different Materials
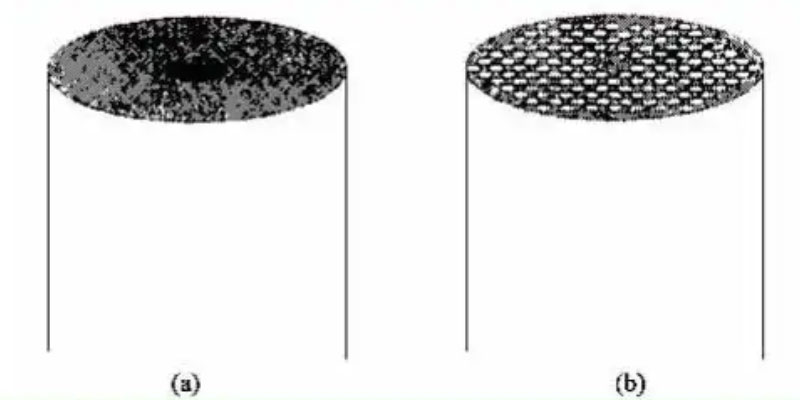
Structure Comparison between Conventional Optical Fiber and Photonic Crystal Fiber
(a) Schematic diagram of the structure of conventional optical fiber
(b) Schematic structure of photonic crystal fiber
Initially, the first photonic crystal fiber (PCF) was manufactured using quartz material. However, this single quartz PCF gradually revealed its limitations in performance, such as a narrow optical transmission window (covering only 0.3~2.5 μm), small third-order nonlinear coefficients, and high phonon energy. In order to overcome these limitations and to meet the higher application requirements, researchers have started to explore the use of other materials for the preparation of PCFs in order to obtain more unique properties.
Phosphate glasses
Tellurite Glasses
Sulfur glasses
- Advantages of Polymer Photonic Crystal Fibers
Polymer photonic crystal fibers (POFs) can be prepared from a wide variety of optically polymeric materials, including polymethylmethacrylate, polycarbonate, polystyrene, COC, and perfluorinated resins, etc. This diversity of preparation materials is what gives polymer POFs their significant advantages. These different polymer materials vary in glass transition temperature, light transmission Abbe number, density, refractive index, coefficient of thermal expansion, water absorption, and mechanical properties, thus providing the flexibility to meet a variety of unique application requirements. Compared to quartz PCFs, polymer PCFs are also more diversified in their preparation process, including drilling, extrusion, mold casting polymerization, injection molding, and other methods can be applied.
3.Applications in Fiber Optic Communication
- Dispersion Compensation and Fiber Lasers
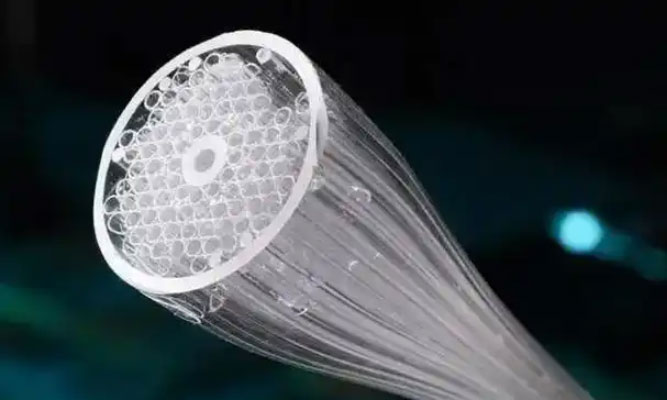

Photonic Crystal Fiber (PCF), as an innovative optical fiber, shows a broad application prospect in the field of fiber optic communication. Its unique structure allows PCF to have excellent optical performance, which has revolutionized the fiber optic communication system. By periodically arranging media with different refractive indices, photonic crystals generate photonic forbidden bands, and photonic crystal fibers take advantage of the center defect to create an optical band.
optlenses
Related Blogs