Advantages and Features of Powell Prisms
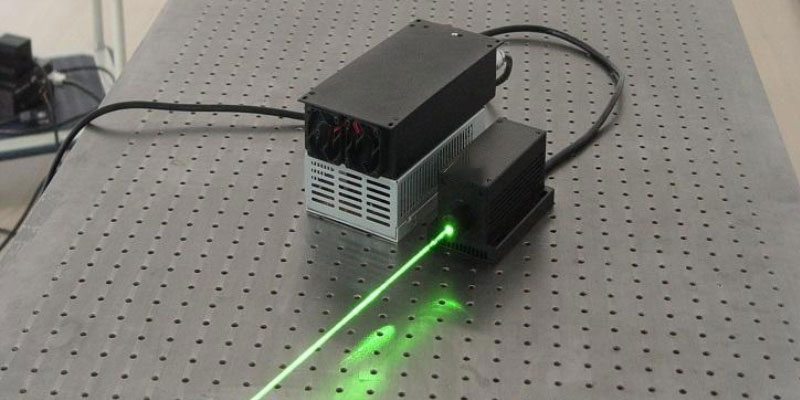
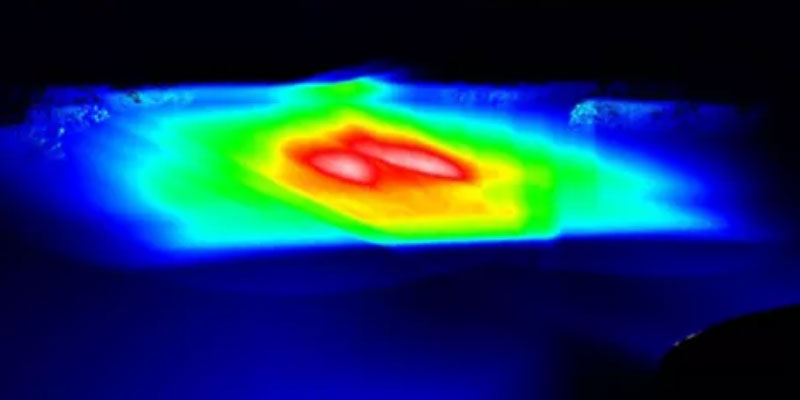
Powell prisms, the masterpiece of optical scribing prisms, enable a laser beam to pass through a line with uniform optical density, excellent stability and superior straightness. Powell prisms solve the problem of conventional Gaussian beams through their two-dimensional aspherical design, providing a more uniform and stable laser line than is possible with conventional cylindrical lenses. Uniquely, the complex 2D aspherical surface design allows the laser to produce rich spherical aberrations as it passes through, thus optimising the distribution of the light path, reducing the light intensity in the central region while increasing the light intensity at the edges, resulting in a uniform and fine straight line. This technological breakthrough plays a crucial role in machine vision applications in many fields such as biomedicine, automotive assembly and food processing.
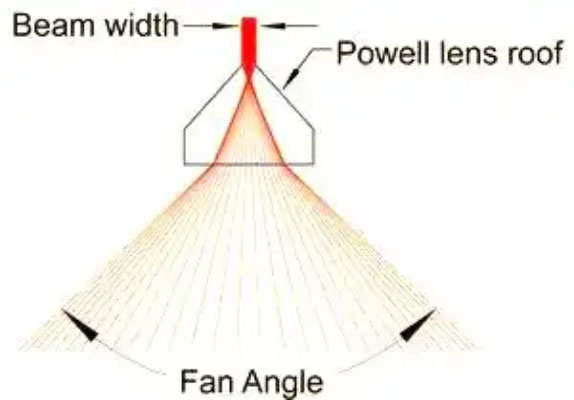
Technical Parameters Impact
The width of the sector angle of a Powell prism is a function of the refractive index of the glass and the angle of the roof. For steeper roofs and higher refractive indices, the fan angle will be wider, resulting in longer lines for a given projection distance. For small fan angles, a mild optical glass with a refractive index of 1.5 is usually used, while for large fan angles a high refractive index of 1.8 or higher is preferred to minimise the effect of steep roof angles on the light.
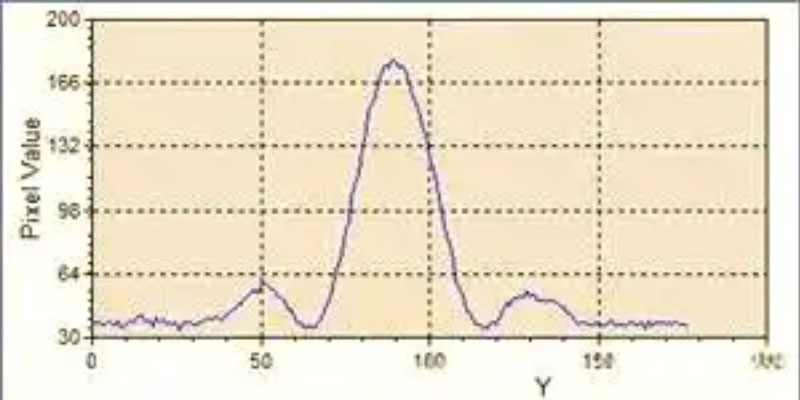
Laser Beam and Application
Laser beam size is an important factor in the thickness of the laser line. For a given projection distance, the size of the incident laser beam will determine the thickness of the laser line. Collimated laser diodes have an elliptical beam profile, allowing a single diode module to provide thin or thick line capability for different applications. Varying the shape of the incident beam adjusts the thickness of the laser line and the depth of focus. As the incident direction of the beam widens, its long axis is perpendicular to the roof of the Powell prism, which in turn creates a laser line with a greater depth of focus and thicker line width. This variation provides the ability to flexibly adjust the laser line characteristics for specific applications.
Optical Path and Installation Considerations
- Optical Path Influences
In exploring the effects of beam shape and direction on laser lines, we have found that a wide or narrow incident beam significantly affects the depth of focus and line width of a laser line. As the beam’s direction of incidence becomes narrower, the way it interacts with the Powell lens also changes significantly. This change not only affects the depth of focus of the laser line, but further alters the linewidth characteristics. By analysing the optical path of the narrow incident beam and the Powell lens, we are able to gain a more precise understanding of the focus and linewidth characteristics of the laser line, which in turn provides more flexibility in adjusting the laser line for real-world applications.
- Mounting and Testing Techniques
The performance and physical properties of Powell prisms are significantly affected by the beamwidth. On a flat outgoing plane, the foot print of the evanescent fan, which serves as the mounting surface, is a critical factor. Extra care needs to be taken during the mounting process to ensure that the mounting hardware does not trap the evanescent light. Additionally, accurate testing and mounting of the diffusion fan angle is critical, especially if the fan angle exceeds 20 degrees, to ensure uniformity of the laser line. Careful handling of diffuse light during installation and testing techniques are critical to assessing uniformity in order to achieve a uniform laser line for exacting application scenarios, which often require matching the Powell lens to the specific beam characteristics of the laser module.
optlenses
Related Blogs