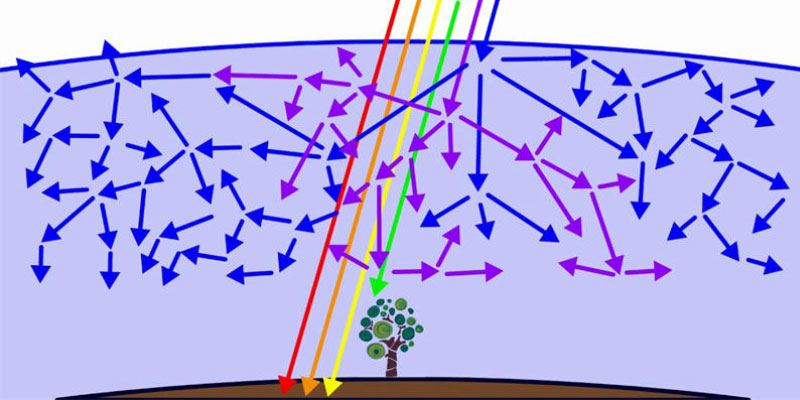
A concave mirror, specifically a concave parabolic mirror, serves to converge light. Its imaging principle relies on reflection, with the resulting image varying according to the object distance. A convex lens, conversely, produces images through refraction. When parallel light strikes its surface, it is reflected and converged at the focal point in front of the mirror. The reflecting surface is concave, with the focal point situated before the mirror. When a light source is placed at the focal point, the reflected light forms a parallel beam. Also known as a concave mirror or converging mirror. The principle of the concave mirror is reflection imaging. A convex lens, conversely, produces refraction imaging. The concave mirror serves to converge light, with the resulting image differing according to the object distance.
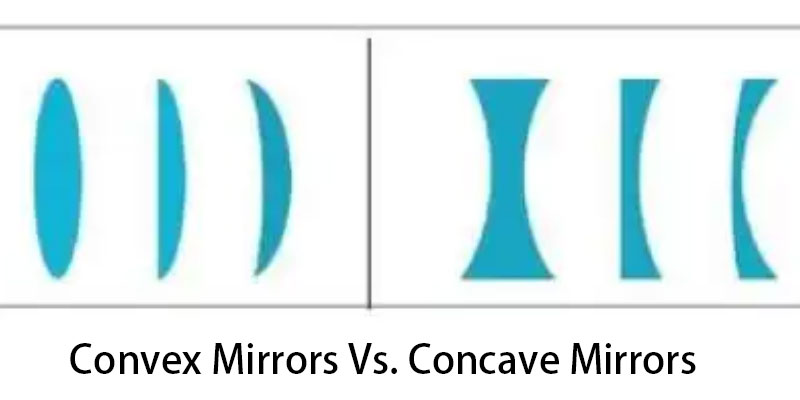
The Difference Between Concave And Convex Mirrors Include: Structural variations. Distinct effects on light. Divergent imaging properties. Divergent focal points. Divergent applications.
Structure differs. A convex mirror consists of a transparent mirror body ground into a spherical surface on both sides. A concave mirror comprises a mirror body with one concave surface and the other opaque.
Effect on light rays differs. A convex mirror primarily refracts light rays. A concave mirror primarily reflects light rays.
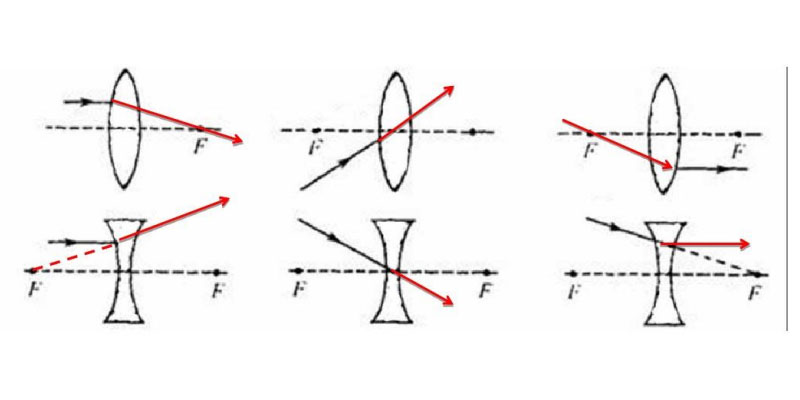
Different imaging properties. A convex mirror produces upright magnified virtual images, inverted magnified real images, inverted equal-sized real images, and inverted reduced real images. A concave mirror can only produce upright reduced virtual images.
Different focal points. A convex mirror has a real focal point and two focal points. A concave mirror has a virtual focal point.
Different applications. A convex mirror is used in spectacles for farsightedness. A concave mirror is used in spectacles for nearsightedness.
Convex Mirror Introduction:
Convex mirrors, also known as wide-angle mirrors, reflective mirrors, or corner mirrors, are spherical mirrors that utilise the outer surface of a sphere as the reflecting surface, thereby producing a diverging effect. Primarily employed at various bends and intersections, they expand the driver’s field of vision, enabling early detection of vehicles approaching from the opposite direction around bends to reduce traffic accidents. They are also utilised in supermarkets for theft prevention and monitoring blind spots. When parallel rays strike a convex mirror, the reflected rays diverge. If extended along the opposite direction of the reflected rays to the rear of the mirror surface, they converge and intersect at a single point. This point constitutes the mirror’s principal focus, which is a virtual focal point.

Convex Mirror Applications:
Convex mirrors find extensive use in applications such as corner mirrors and wide-angle mirrors. The most common examples are rear-view mirrors and funhouse mirrors, which exploit the principle of light divergence to broaden the field of vision, thereby facilitating better awareness of vehicles behind. (The back of a spoon functions as a convex mirror, while its concave front acts as a concave mirror.) Objects viewed through a convex mirror always appear distorted.
Concave Mirror Introduction:
Concave Mirror Characteristics:

Reflection phenomena on concave mirrors adhere to the laws of reflection.
Light rays parallel to the principal axis converge at the focal point after reflection. This focal point represents the actual convergence of light rays, thus constituting a real focal point.
Concave mirrors converge light rays; consequently, a shorter focal length indicates greater converging power.
Concave and convex mirrors both fall under the category of spherical lenses, differing in the paths light takes when refracted. Consequently, they serve distinct groups of people: one is suitable for myopia, while the other addresses hyperopia and presbyopia. Thus, the distinction between concave and convex mirrors lies in the differing paths of light and refraction, as well as their respective user groups and conditions. Nevertheless, both are spherical lenses designed to correct refractive errors.
optlenses
Related Blogs