Dichroic mirrors, as a powerful assistant in gemstone identification, are widely used to observe the polychromaticity of gemstones. The principle of operation of this conventional testing instrument is based on the detection of gemstones with specific optical properties. It is important to note that only single-crystal stones with color, transparency and birefringence can exhibit the optical phenomenon of polychromy.
The dichroic mirror, a powerful tool for gemstone identification, is widely used for the observation of polychromy through its specific optical principle. It is capable of detecting stones with specific optical properties, providing a powerful support for the identification process. It is worth noting that only single-crystal gemstones with color, transparency and birefringence can exhibit the wonderful optical phenomenon of polychromy.
1.Exploration of the principle
When natural light enters a non-homogeneous gemstone, it is broken down into two beams of polarized light whose vibration directions are perpendicular to each other, and the propagation paths of these two beams of light are also different. Due to the anisotropic nature of non-homogeneous gemstones, they absorb light in different vibrational directions to different degrees. By somehow separating these two polarized lights, we can observe the different colors presented by the gemstones.
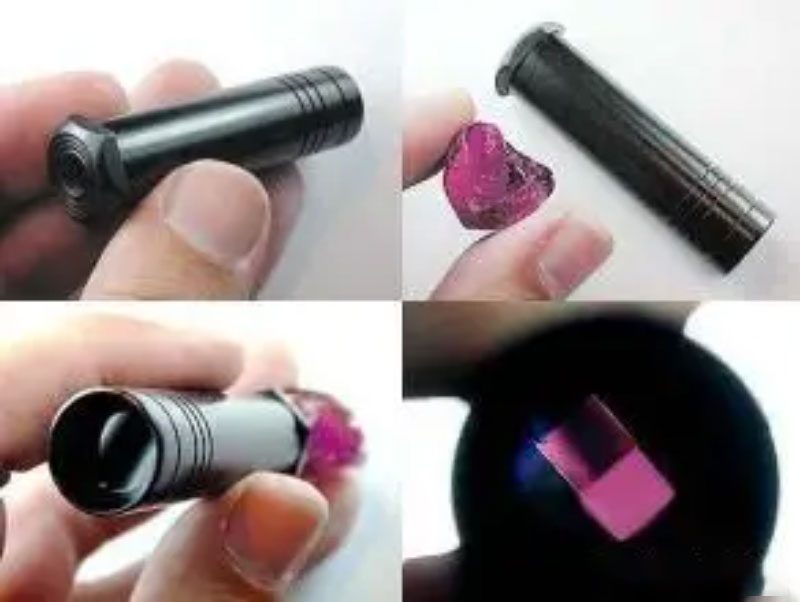

2.Dichroic Mirror Structure in detail
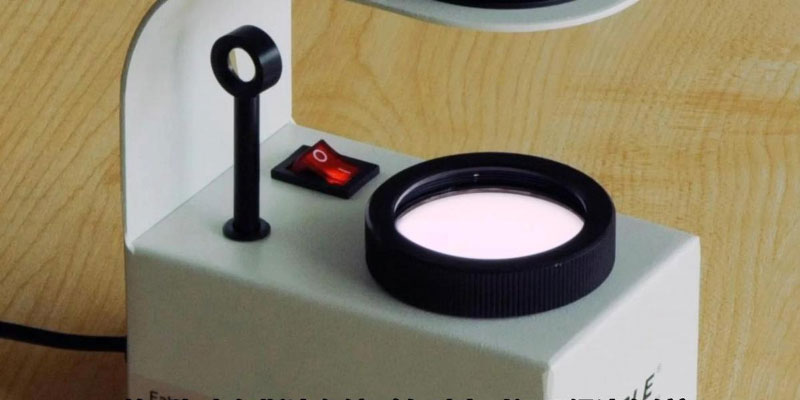
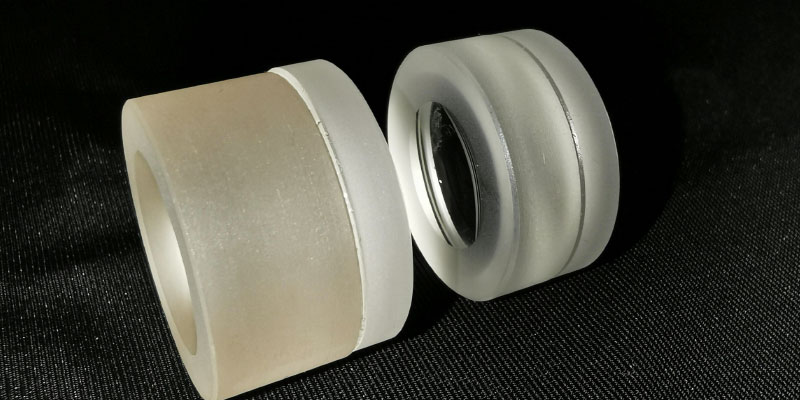
The construction of a dichroic mirror consists mainly of components such as glass prisms, icosahedral rhombohedrons, lenses, windows, and eyepieces (see Figure 2). The icosahedron plays a crucial role in distinguishing the two beams of plane-polarized light passing through the stone and visually comparing the colors of the two beams side by side.
The dichroic mirror is a delicate and complex construction, consisting of a glass prism, an icosahedron, a lens, a window, and an eyepiece. The clever combination and synergy of these components allows the dichroscope to accurately observe and compare the subtle internal features of gemstones. Among them, the unique nature of the icosahedron as a key component enables it to effectively differentiate the two beams of plane-polarized light passing through the gemstone, thus forming side-by-side colored light bands in the eyepiece, providing the observer with intuitive and detailed comparative information.
3.Application value
Polychromy has an important value in gemstone identification and evaluation. By observing the intensity and color change of polychromy, the variety, quality and rarity of gemstones can be judged more accurately. At the same time, polychromy is also an important part of the charm of gemstones, which can enhance the visual effect and attractiveness of gemstones.
Identifying strongly polychromatic gemstones: Cordierite, for example, displays remarkable trichromaticity, including blue, violet-blue and light yellow, which helps to identify its variety.
Distinguishing isotropic from anisotropic gemstones: rubies and red spinels are similar in appearance, but can be easily distinguished by observing the polychromy. Rubies are distinctly dichroic, while spinels exhibit isotropy in all directions and no polychromy.
optlenses
Related Blogs