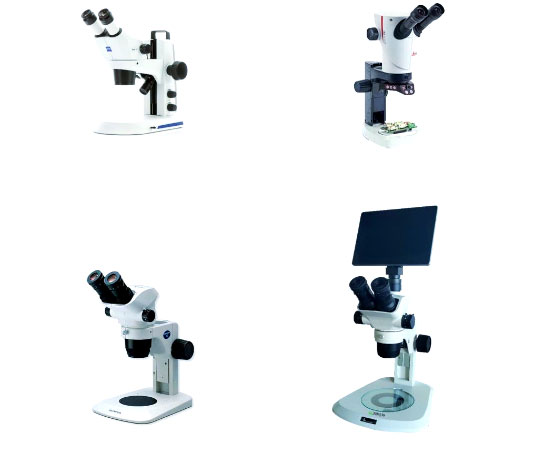
Overview of Stereo Microscopes
A stereo microscope, also known as a ‘real-image microscope,’ ‘stereoscopic microscope,’ or ‘dissection microscope,’ is a precision instrument capable of providing a three-dimensional image. It has a wide range of applications across various fields, including macroscopic surface observation of materials, failure analysis, fracture analysis, as well as biology, medicine, agriculture, forestry, and industry. Its unique feature lies in the use of two independent optical pathways. Through a zoom lens system, the two light beams formed after imaging the object are separated and create a certain stereoscopic angle, typically between 12 and 15 degrees. This design ensures that each eye perceives a slightly different image of the specimen, allowing the brain to fuse these images to reconstruct the object’s three-dimensional stereoscopic perception. Therefore, stereomicroscopes excel in operations requiring interaction with specimens, such as dissection, sorting, micro-carving, and micromanipulation, making them indispensable tools.
The optical path design of stereomicroscopes encompasses two primary types: the Greenough design and the Galileo design (CMO design). The schematic diagram of the Greenough design is as follows:
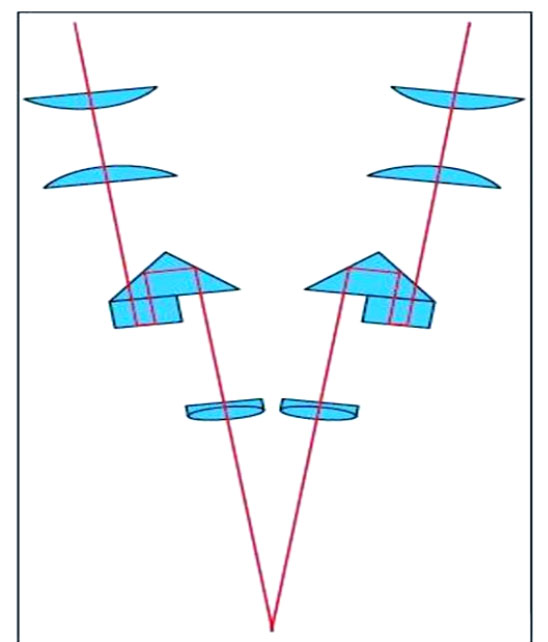
The core of the Greenough principle lies in two identical optical systems connected to the same mount at a small angle of 10 to 16 degrees. This design allows the two imaging prisms in the optical path to work in tandem, ensuring that the observed image remains upright and aligned with the actual object’s orientation. In fact, most conventional stereo microscopes widely used in the market are designed based on this principle. It is worth noting that many well-known microscope brands both domestically and internationally, such as Leica and Nikon, also adopt the Greenough principle in their stereo microscope products.
By observing the imaging effect diagrams of the HZ6100, we can clearly see its exceptional imaging quality. Based on the Greenough principle, this microscope achieves high-resolution, high-contrast imaging effects through precise craftsmanship and high-quality optical components, providing researchers with accurate and reliable observation data.
Stereo fluorescence imaging effect diagram
While discussing the Galilean optical path principle and the upgrading of stereo microscopes, we present an effect diagram of stereo fluorescence imaging. This diagram clearly demonstrates the microscope’s outstanding performance in fluorescence imaging, providing researchers with an intuitive visual reference.
Wide application of stereomicroscopes

Stereo microscopes have a wide range of applications across multiple fields. They are not only used in research areas such as zoology, botany, entomology, histology, mineralogy, archaeology, geology, and dermatology, but also serve as an essential tool in the textile industry for inspecting raw materials and cotton and wool fabrics. In the electronics industry, stereomicroscopes are indispensable, frequently used for operations such as transistor spot welding and inspection. Additionally, it can be used to examine surface phenomena such as crack structures, pore shapes, and corrosion conditions in various materials. In the manufacturing of small precision parts, the stereomicroscope is also indispensable, serving for the installation of machine tools, observation of work processes, inspection of precision parts, and assembly tools. It can also be used for quality checks on the surfaces of lenses, prisms, or other transparent materials, as well as precision scales. Furthermore, stereomicroscopes play a significant role in cultural relic authentication and the retrieval of criminal evidence in forensic investigations. In summary, stereomicroscopes have been widely applied in numerous fields, including textile products, chemical engineering, plastic products, electronics manufacturing, mechanical manufacturing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, printing, higher education institutions, and archaeological research.
optlenses
Related posts
Stereo Microscope:Optical Principles,Various Applications and Common Types
What are laser modules and laser diode z?
What types of landscapes are fish eye lens suitable for?
What is the function of a magnify glasses?


